Relief for Bowel Incontinence
Personalized care to help you regain control and confidence
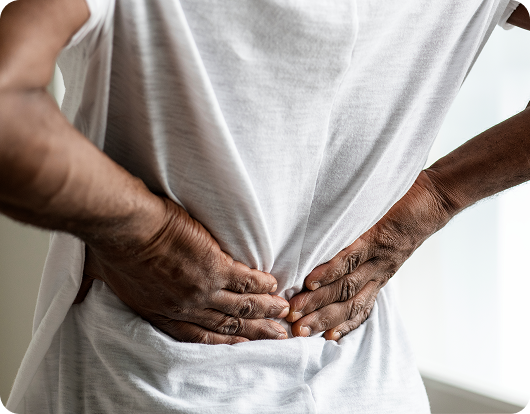
Understanding Bowel Incontinence
Bowel incontinence is a condition where individuals lose control over their bowel movements, resulting in the involuntary leakage of stool. Its severity can range from occasional minor accidents to a complete loss of control.
These unexpected episodes can deeply affect daily routines, independence, and overall quality of life. Seeking prompt, appropriate treatment is essential to reduce symptoms and restore confidence.
Understanding Bowel Incontinence
Bowel incontinence is a condition where individuals lose control over their bowel movements, resulting in the involuntary leakage of stool. Its severity can range from occasional minor accidents to a complete loss of control.
These unexpected episodes can deeply affect daily routines, independence, and overall quality of life. Seeking prompt, appropriate treatment is essential to reduce symptoms and restore confidence.

Causes of Bowel Incontinence
Bowel incontinence may result from a variety of physical or neurological issues, including:
Muscle damage – Injury to the anal, pelvic floor, or rectal muscles can reduce your ability to control bowel movements.
Nerve damage – Nerves coordinate the contraction and relaxation of the rectum, anus, and pelvic floor muscles. Damage to these nerves can impair this coordination.
Loss of rectal elasticity – Scarring or stiffening of the rectum can reduce its ability to stretch, causing it to fill too quickly and leading to leakage.
Health Conditions That Cause Bowel Incontinence
Several health conditions and digestive disorders can interfere with normal bowel function:
Chronic constipation – can stretch and weaken rectal muscles and nerves, especially when large, hard stools are difficult to pass.
Diarrhea – produces loose stools that are harder to retain, often worsening symptoms.
Rectal prolapse – occurs when the rectum descends through the anus, stretching and potentially damaging nerves.
Hemorrhoids – may prevent the anus from closing properly, allowing leakage.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) – can cause alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea, complicating control.
Bowel Incontinence After Childbirth
Bowel incontinence is a common occurrence among women following childbirth. The process of giving birth places significant pressure on your pelvic floor muscles and surrounding structures. It can potentially compromise your ability to maintain bowel control.
Childbirth can lead to:
Tearing or stretching of pelvic floor muscles during delivery
Pressure-induced nerve damage
Hormonal changes during pregnancy and postpartum
Perineal tears or surgical incisions
Post-delivery issues like constipation or diarrhea
These factors can compromise bowel control and may require medical intervention.
Treatment Options for Bowel Incontinence
A tailored treatment plan depends on the underlying cause and severity of your symptoms. Management typically combines lifestyle changes, therapeutic techniques, and medical interventions.
Dietary Changes
Adjusting your diet can help restore regular bowel function. Increasing fiber intake promotes stool consistency and regularity. Avoiding trigger foods such as alcohol, dairy, greasy or spicy meals, and caffeine may reduce episodes. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can also ease symptoms.
Pelvic Floor Exercises
Also known as Kegel exercises, these target and strengthen the muscles that support your rectum, bladder, and pelvic organs. Strengthening these muscles enhances bowel control.
Medication
Depending on your condition, medications can:
Slow stool movement through the digestive system
Reduce frequency and improve consistency
Stimulate bowel movements to aid regularity
When combined with lifestyle changes and exercises, medications can significantly improve outcomes
Biofeedback
Biofeedback therapy teaches better control over pelvic floor and anal sphincter muscles. Using sensors and visual or auditory cues, patients learn how to activate and coordinate muscles for improved bowel regulation.
Diabetes
Multiple sclerosis
Parkinson’s disease
Alcoholism
Spinal cord injuries or back surgery
Pelvic trauma or previous surgeries
Surgery
If conservative treatments are unsuccessful, surgical options may be considered:
Sphincteroplasty: Repairs damaged anal sphincter muscles to enhance control.
Colostomy (bowel diversion): Redirects stool through an abdominal opening into a collection bag.
Axonics Therapy: Advanced, Minimally Invasive Relief
Axonics Therapy for Urge Incontinence
For patients who do not respond to conservative treatment, Axonics Therapy provides a minimally invasive, long-term solution. This therapy works by sending mild electrical signals to stimulate the sacral nerves, improving communication between the brain and bladder.
The procedure involves implanting a small device in the lower back area, near the sacral nerve roots. At Northwest Continence Center, our surgeons specialize in this type of advanced procedure. We ensure the highest standards of precision, care, and expertise to maximize safety and outcomes.
Why Patients Trust Northwest Continence Center
We take a science-based, compassionate approach that puts your comfort and results first.
Advanced Axonics Therapy
A minimally invasive solution that restores nerve communication for lasting relief.
Personalized, Science-Based Care
Every treatment plan is tailored to your unique needs using proven medical approaches.
Experienced, Specialized Providers
Our experts are trained in continence-focused procedures and neuromodulation techniques.
Judgment-Free Patient Support
We create a respectful, compassionate environment where you feel safe and heard.
We’re More Than Just a Clinic
We understand that incontinence can be emotional and isolating. That’s why we’re committed to making your experience safe, respectful, and empowering. Every visit is designed to make you feel heard and supported.

Let’s find the right solution together.